Powerhouse Arts/
Herzog & de Meuron
Project Details

Location(City/Country):
Brooklyn, New York / United States
Tipology:
Cultural
Year (Design/Construction):
2016 / 2022
Area (Net/Gross):
16270 m2 / -
Operational Carbon emissions (B6) kgCO2e/m2/y:
-
Embodied Carbon emissions (A1-A3) kgCO2e/m2:
-- The flexibility of the space will help to ensure its future use.
- Preservation of existing materials and structure is a core value at the heart of this retrofit.
Powerhouse Arts is a not-for-profit manufacturing facility based in Gowanus and Red Hook, Brooklyn, New York, established to create a robust platform for art production and employment in the arts. Consisting of 170,000 square feet of workshop space for fabrication in wood, metal, ceramics, textile and print, the redevelopment project transforms an existing, derelict structure on a contaminated site into a hub for artists, fabricators and other workers
and ensures that the industrial legacy of the site will extend into the next century. Reimagining a 115-year-old power plant as a modern production facility, the project aims to maintain a manufacturing presence in a historically industrial part of Brooklyn. By preserving, restoring, and reconstructing essential elements of the original power station, the project strengthens the building’s industrial character and its relationship to the immediate urban context.
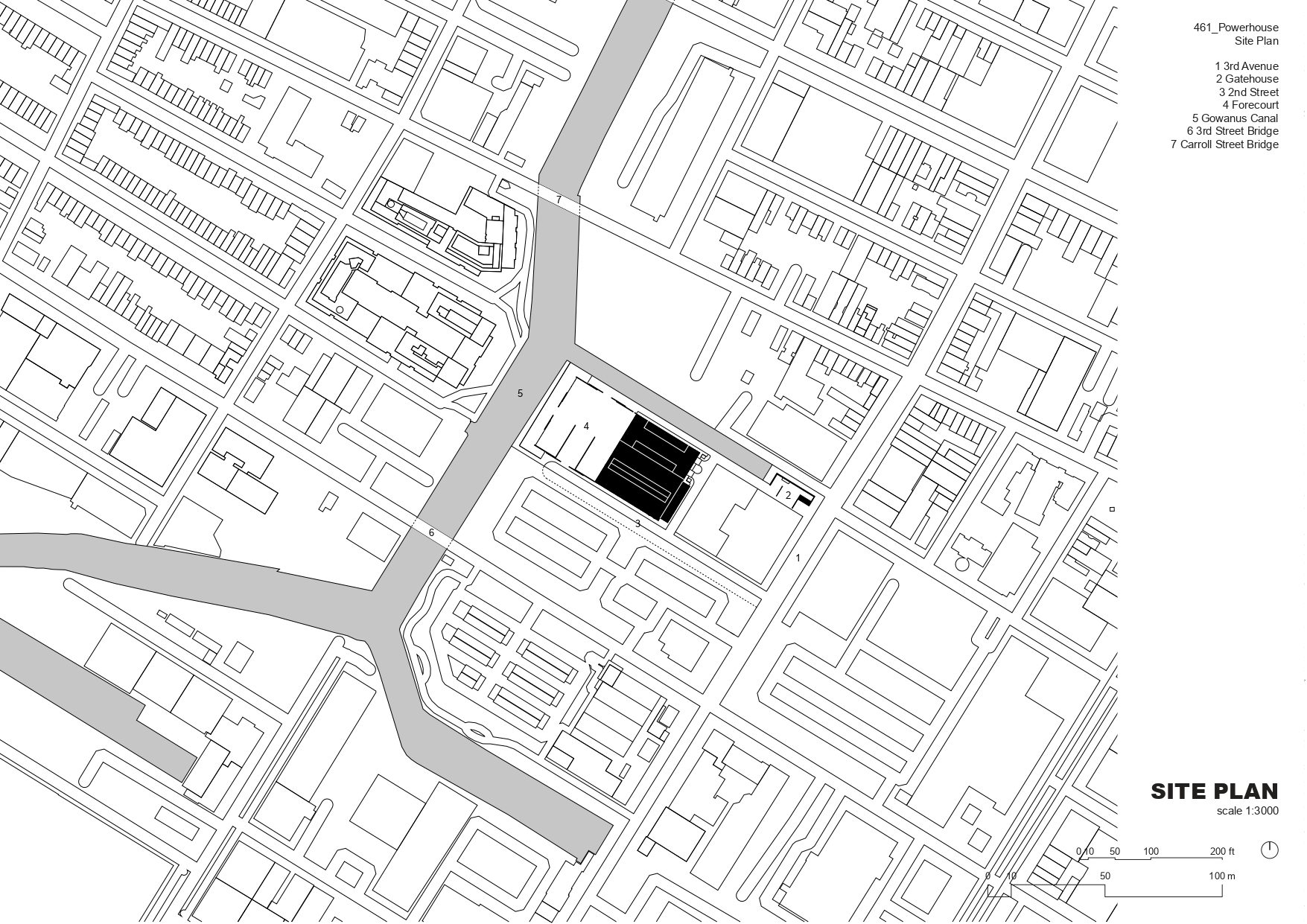
The project is situated along the Gowanus Canal, a natural low point between the neighbourhoods of Red Hook and Carroll Gardens to the west and Park Slope to the east. In 1904, the Brooklyn Rapid Transit Power Station, designed by Thomas Edward Murray, was completed on the site to serve the expanding transit system of Brooklyn.
Decommissioned in the 1950s, half of the original structure – the Boiler House – was demolished, leaving the Turbine Hall to stand by itself. In the late twentieth century, the remaining structure became a destination for local graffiti artists, and it earned the nickname of “The Batcave.” Subsequently, the Gowanus Canal was designated a Superfund site in 2010 by the United States Environmental Protection Agency, identifying it as a candidate for remediation. Prior to the start of construction, the site contamination was resolved through completion of the New York State Brownfield Cleanup Program. In April 2016 – after an initial selection process that included a concept design for the site – Herzog & de Meuron was appointed as design consultant for the project.
A mix of storage sheds, warehouses, and mixed-use, commercial buildings, the neighbourhood is rapidly gentrifying. The existing building is set back from the edge of the Gowanus Canal to the west and bound at the north by First Street, at the south by Second Street, and at the east by a large storage building along Third Avenue. The scale of the Turbine Hall and its location atop relatively high ground give it a visual prominence in the neighbourhood.
The industrial landscape and history of the site play a pivotal role in the design proposal. It reinterprets the historic Boiler House by reinstating its mass and re-establishing its relationship with the existing Turbine Hall. The Turbine Hall is preserved – stabilised and strategically repaired – and its historical layers are integrated into the new manufacturing facility.
The reinstated Boiler House bears on the existing, historic foundations, minimising further site excavations. Its concrete façade responds to the existing masonry shell of the Turbine Hall and provides a durable and straightforward envelope for the addition. The exposed structure at the interior, comprising concrete columns and slabs, provides flexible spaces for workshop use. The historic, punched openings of the Turbine Hall are incorporated
into the Boiler House envelope, and the openings of both buildings are filled with new windows.
Atypically for an industrial project, the respective fabrication shops are stacked vertically with the disciplines requiring the most clear height and best access to the loading areas – that is, the metal and wood workshops – located on the ground floor, while the disciplines with the most stringent exhaust requirements – print, textile and ceramics – are located at the top floors of the Boiler House. Adhering to the best practices of industrial hygiene (refined through consultation with several specialists), a large amount of air is exhausted from the building to ensure contaminates from the manufacturing processes do not adversely affect the interior work environment. To that end, the workshops share a common, large vertical service wall that also contains the vertical circulation elements, stairs and elevators, as well as the restroom plumbing stack. The consolidation of these vertical elements between the existing and the new building provides additional lateral, structural stability for both buildings and creates the flexibility required for workshop programming within the remainder of the Boiler House floor slab. Two large bulkhead volumes at the roof express the primacy of the mechanical, electrical, plumbing, and fire protection systems in the project and recall the
historic smokestacks of the original Boiler House building. They also illustrate the resiliency of the facility, as no equipment has been installed at the base of the building given the potential for flooding and sea level rise in the future.
To the west of the project along the Gowanus Canal, a forecourt provides flexible outdoor work and storage space as well as loading for material deliveries. To the east of the project, closer to the approach to the site from public transit, a new opening into the masonry envelope of the Turbine Hall serves as the primary public entrance. Upon entering
the building, the visitor is confronted with the juxtaposition of historic details – concrete vaults, brick chases, and glazed tilework – residual graffiti and the new architectural elements. A large, concrete shear wall forms a vertical space beyond the entrance lobby and a metal stair draws attention upward to the grand hall, the main public feature within the building. The entire upper level of the Turbine Hall building preserves the original spatial composition of the historic structure, exposing the refurbished, steel trusses overhead, and providing a multifunctional space for exhibitions and events. An adjacent, double-height volume in the Boiler House serves as the intersection of the public and workshop functions in the building, providing additional room for exhibitions, events, staging, and assembly.
- Partners: Jacques Herzog, Pierre de Meuron, Ascan Mergenthaler .
- Project Team: Philip Schmerbeck (Associate, Project Director), Jack Brough (Project Manager, SD – CA), Raha Talebi (Project Manager, Competition – Pre-SD) Farhad Ahmad, Bruno de Almeida Martins, Iwona Boguslawska, Christopher Cornecelli, Lasse Deichmann, Muriz Djurdjevic, Nazli Ergani, Florian Frank, Fabiola Guzman-Rivera, Josh Helin, Magnus Overby, Pedro Peña Jurado, Martin Jonathan Raub, Rebecca Roberts, Emma Thomas, Pimchanok Wangveeramit, Samuels Zeif.
- Photographer: Albert Vecerka/ESTO