Courtyard Houses
News Detail

Source:
Aida Zare
 Saadat House, Shiraz, Iran. The courtyard is attached to a closed space with the eivan; which is a roofed semi-open space extended across the northeastern side of the courtyard and acts as a shading device.
Saadat House, Shiraz, Iran. The courtyard is attached to a closed space with the eivan; which is a roofed semi-open space extended across the northeastern side of the courtyard and acts as a shading device.
Courtyard Houses are one the oldest types of human places of residence and are widespread in different countries and cultures, from Jordan to China. The main part of the buildings in this kind of houses, is arranged around a central yard. They represent a nice hierarchy of open, semi open and closed spaces and invite nature to indoor spaces by embracing the central garden. The cultural and climatic values of courtyard houses have been reviewed in recent years according to their socio-ecological aspects. The focus of this writing would be on how this type of architecture can provide high quality indoor spaces especially in hot climatic zones.
A central courtyard is one of the main elements in traditional buildings in many countries like Egypt, Japan, Spain and Iran. They can be a very nice tool to moderate the outdoor harsh climatic conditions, whether hot or cold. In fact, by using massive masonry walls in its surrounding, and planting trees and vegetation, courtyards mild the humidity and air temperature and make a desirable microclimate in the middle of the building to face indoor spaces. Creating green areas supply more shades in summer and avoid entering the direct sun into indoor spaces while decreasing the air temperature. In some hot cities like Yazd or Kashan in Iran, courtyards are located underground and contain a pool. This design strategy reduces the air temperature noticeably in summer using geo-cooling and also evaporative cooling. In addition, it can provide heat and humidity in dry and cold winters of the area. The organization of spaces and selecting the type of the trees on each side of the yard is very important to improve its climatic function. The north side of the yard is filled with deciduous trees, to bring more shade in summer and let the direct sun enter the south windows in winter. Planting fruit trees and vegetables in the yards, can supply foods for inhabitants besides all the benefits of gardening.

Borujerdi House, Kashan, Iran. The underground courtyard with a fountain pool and the windcatcher are among passive cooling tools that are used to moderate the extra hot air temperature. Photo ref: Sobhan Zare Mohazabiye.
Courtyard houses can act as an effective passive system to moderate the climatic condition, and as they make a nice interaction between nature and indoor spaces they bring light, fresh air, calmness, privacy and beauty for the residents. Hence they improve indoor environmental quality by ameliorating thermal comfort, daylighting, view, and biophilia. Using this type of architecture would enhance biodiversity, decrease the UHI effect, and also improve the cultural values of each city.
References:
Ghiabaklou, Zahra. (2014). Fundamentals of Buildings Physics 4: Passive Cooling. ACECR Publication. Amirkabir University.
Memarian, Gh. Hossein. (2021). Courtyard House: With Special Reference to Shiraz. Goljam Publication. Tehran.
Ganjnameh Cyclopedia of Iranian Islamic Architecture, Volume 16 Houses. (2016). Shahid Beheshti University.
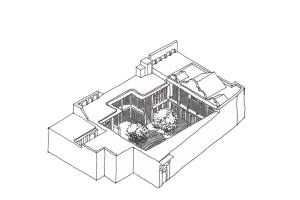 Saadat House, Shiraz, Iran. The courtyard is attached to a closed space with the eivan; which is a roofed semi-open space extended across the northeastern side of the courtyard and acts as a shading device.
Saadat House, Shiraz, Iran. The courtyard is attached to a closed space with the eivan; which is a roofed semi-open space extended across the northeastern side of the courtyard and acts as a shading device.